Conveniently located to serve Kelowna, BC.
Treatment Options
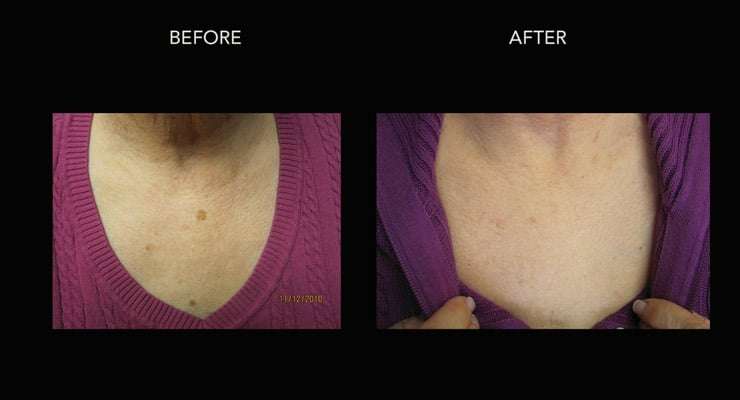
Melasma Treatment
We will help you reduce your melasma to feel more confident and reduce the need to cover up. Melasma is a difficult condition to treat but we can usually lighten this pigmentation over a series of very special and gentle laser treatments combined with topical skin care products.